Aspects of soil characters in maize cultivation
For the farmer, soil is the most important factor of production. Maintaining the soil is the basis for the profitability of the farm.
The following aspects should be considered:
- Maize is a warmth-loving, tropical crop
- Rapid warming of the ground in spring is necessary
- Rapid germination
- High field emergence
- Rapid development of the young plants
Each soil type is characterised by different properties.
These properties have advantages as well as disadvantages for
soil preparation and cultivation of crops.
The following table lists these advantages and disadvantages to give you an overview of the characteristics of
various soils.
Advantages and disadvantages of different types of soil
| Soil type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| mild | Heating, machinability | Water deficiency, nutrient shift |
| Average | Water, nutrients, workability | – |
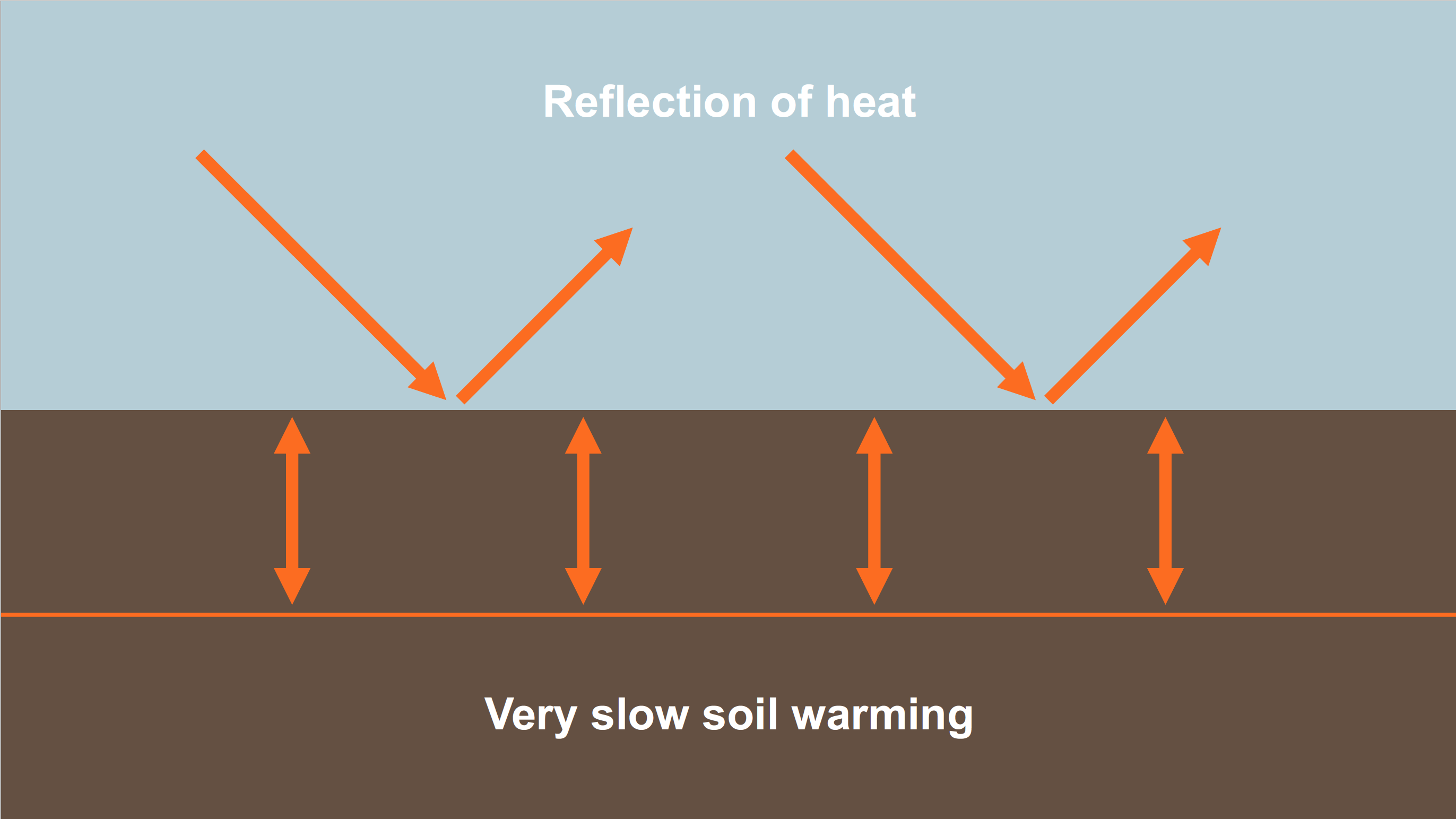
| severe | Water, nutrients | slow heating, encrustation, compaction |
| Moorland | Water | slow warming, late frosts, pH-values |
| Waterlogging, compacted soils | – | Slow warming, slow mineralisation, unfavourable crumb structure |
Source: KWS SAAT SE & Co. KGaA
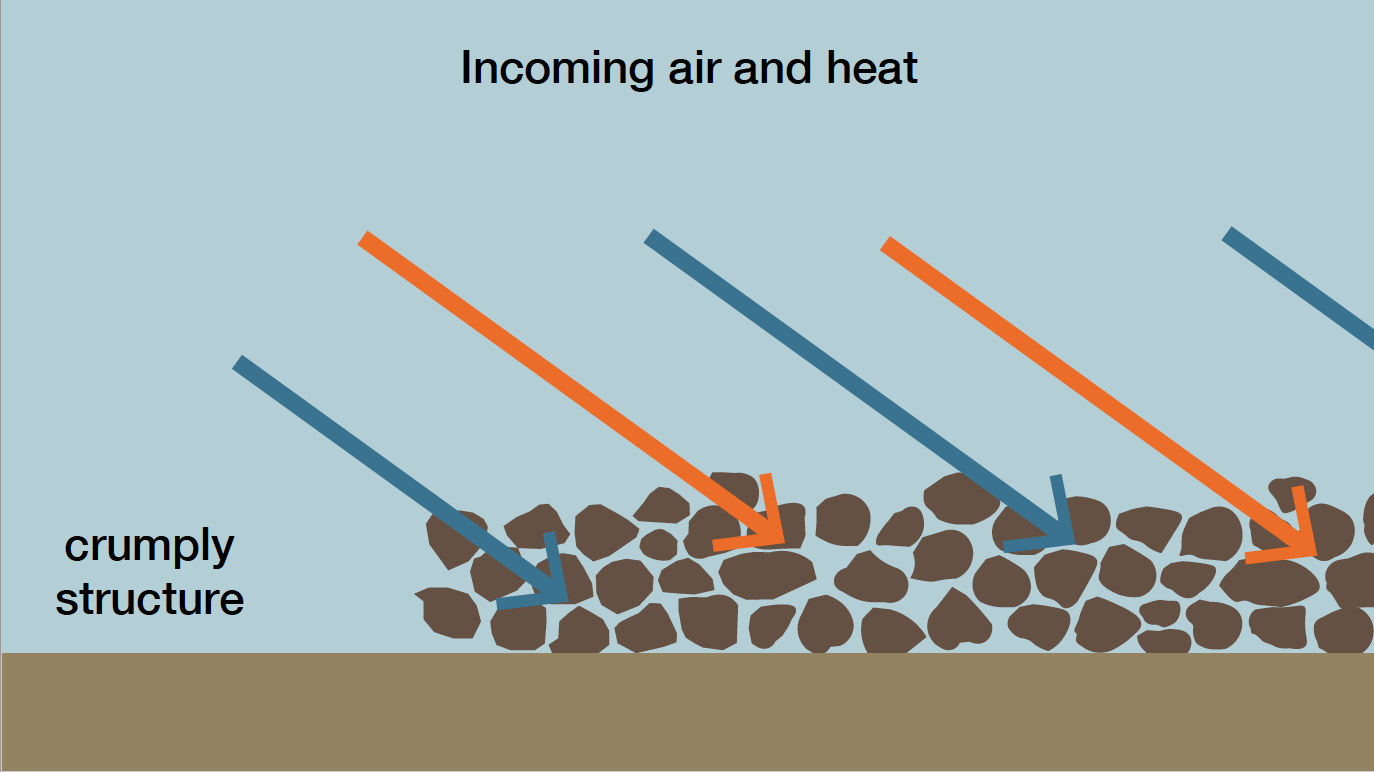
The optimal soil for maize cultivation is
- relaxed
- compression free
- crumbly
Consequences of compaction include
- Soaking and erosion
- Oxygen deficiency in the soil
- Reduction of the activity of microorganisms
- Disruption of mineralisation
- Limitation of rooting
- Interruption of capillary rise of groundwater
This in turn leads to:
- Nutrient deficiency
- Pitchering and leaf discolouration
- Significant shortfalls
Countermeasures:
1. Deep loosening
2. Soil-friendly tyres
3. Increase the humus content with catch crops, organic fertilisation and adjustment to the right pH-value