Line breeding
Overview
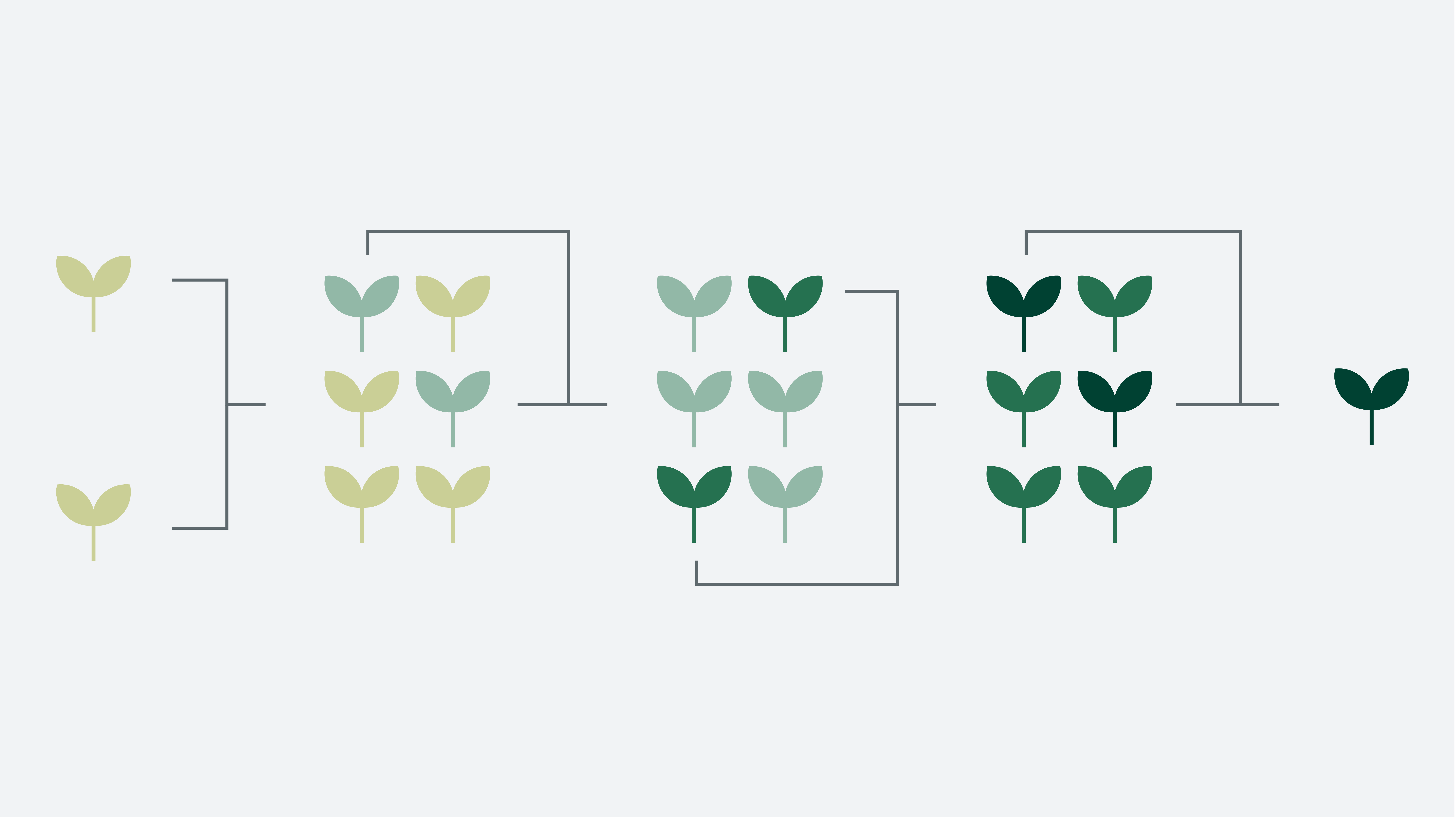
In a nutshell
Here you crossbreed two parent lines that complement each other as much as possible in desired properties. From the offspring, homozygotic plant lines are developed, so-called line-bred varieties.
Advantages
Line-bred varieties are very homogeneous and the offspring of the plants are genetically stable.
Disadvantages
Time-consuming: Several cycles/generations must be cross-bred and bred through self-fertilisation before the desired result is achieved.
Development
Self-pollinated varieties in traditional agriculture, so-called landraces, consist of mixtures of lines. Line-bred varieties have in a sense developed from them.
Application at KWS
Barley and wheat breeding
An overview of our breeding methods
Your contact